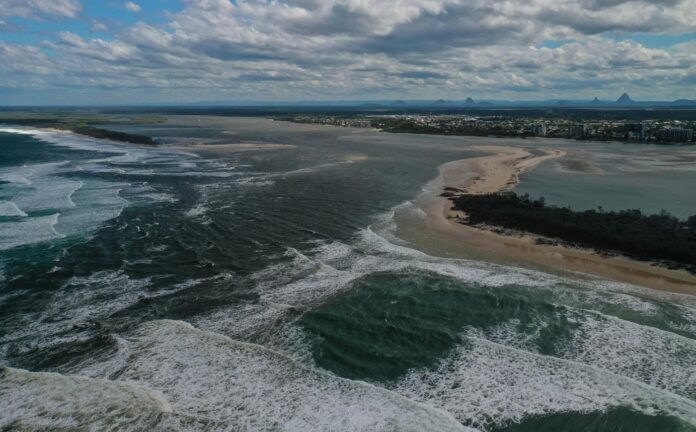
A review of the causes of erosion that led to a tidal breakthrough at Bribie Island has shed more light on the event.
A 48-page report, by maritime design house and technical consulting firm BMT, was delivered to the Department of Environment and Science, after the ocean crashed its way through the northern end of the isle early last year.
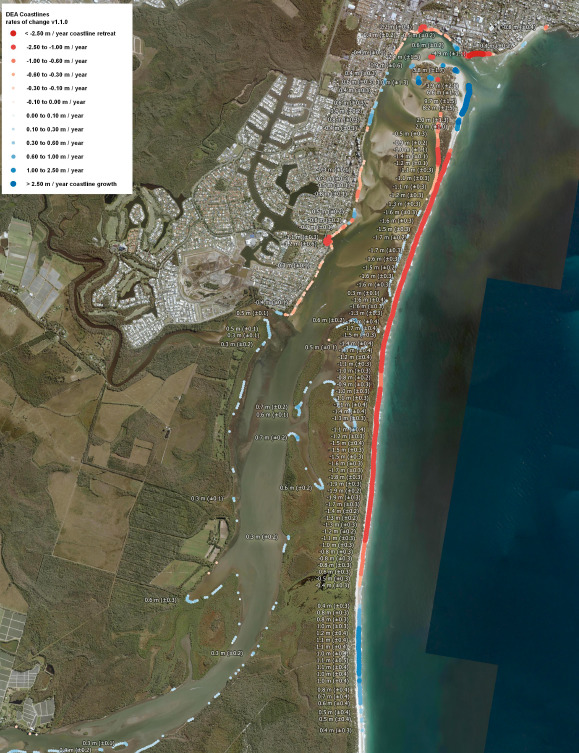
The Review of Causes of Northern Bribie Island Erosion said that erosion had been an issue there for decades and that after the breakthrough there was considerable community angst about the perceived loss of coastal protection to the mainland, provided by the island, and a desire to understand the causes of erosion that led to the breakthrough.
It said the DES was of the view that erosion along the island was due to natural causes, but some community members suggested a possible human cause.
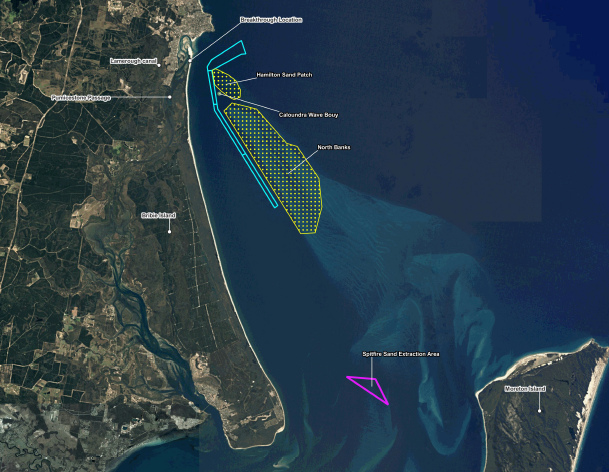
BMT was tasked to study the impacts of natural coastal processes, dredging at the Spitfire Sand Extraction Zone, dredging at the Northwest Channel, vessel traffic and the development of Lamerough Canal.
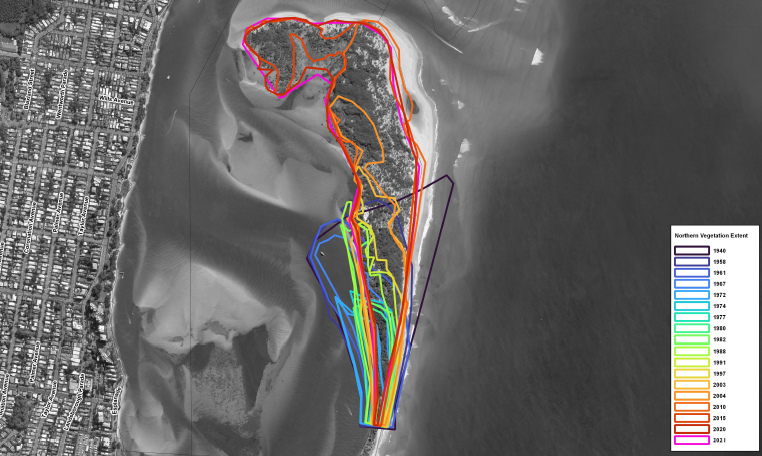
The review utilised bathymetric (ocean and river floor) surveys, coastal datasets, coastal process models, historical aerial photographs and information obtained from experts to investigate each of the possible causes.
It found that large waves on the isle’s eastern side and channel migration within the Pumicestone Passage on the isle’s western side were the primary causes of long-term erosion, which led to the breakthrough.
“Erosion from waves, and in particular large waves from tropical lows or cyclones, is not sufficiently counterbalanced by subsequent accretion (build-up of sand), leading to a long-term negative sediment budget and therefore overall erosion of the eastern shoreline,” the report said.
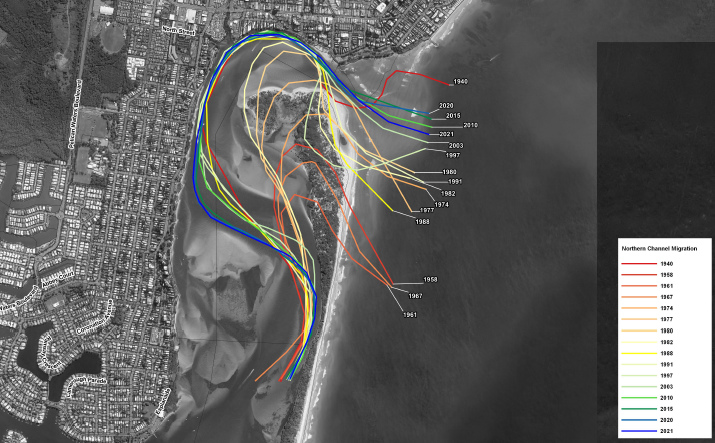
“The western shoreline has eroded as a result of the migration of the channel, forced by the growth and migration of sand shoals in the northern part of the passage.
“These two natural processes have resulted in a consistent trend of erosion from the 1940s to the present time and are identified as the leading cause of erosion on the northern portion of Bribie Island.”
The review found no evidence to suggest dredging in the Spitfire area impacted the island, due to distance and sand migration patterns, and that dredging in the Northwest Channel did not appear to contribute to erosion either, with exposed rock patches indicating negligible rates of sediment transport.
The review found that wake from large vessels offshore did break on the shoreline of the island but with minimal impact, while wake from smaller vessels within the passage contributed a minor amount of erosion.
The report said the development of Lamerough Canal created additional tidal volume within the passage, but it appeared to have no significant influence on tidal flow in the passage.
The review then summarised the causes of erosion.
“The major contributions to erosion of northern Bribie Island are from growth and migration of the sand shoals within northern Pumicestone Passage (predominantly via sand migrating north from Bribie Island and south from Kings Beach), changing the orientation of the channels from running north-south to east-west, forcing flood tide flows to directly impact on the western shoreline of Bribie Island (and from) erosion of the open coast shoreline by waves, particularly those from tropical low and tropical cyclone conditions.”
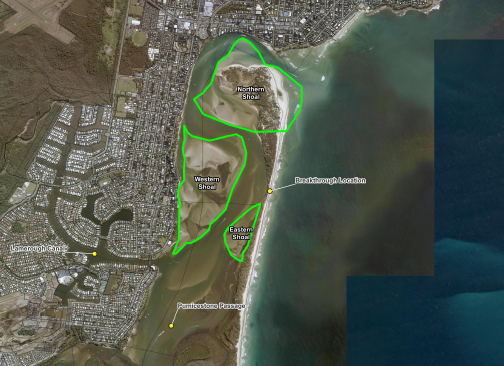
“The complex interaction of waves and tidal currents migrate sand north into the Pumicestone Passage entrance and south along Bribie Island, with very little sand returned, resulting in a continuous sand deficit and shoreline recession of the eastern beach.
“The investigations also noted that there were other causes that showed a plausible contribution to erosion of Bribie Island, but that the contribution was insignificant in magnitude.”
The review said further investigations could be done to get “a detailed understanding of how the new arrangement of Bribie Island has changed the local coastal processes”.
It suggested coastal monitoring and a more detailed boat wake erosion study and a more detailed Lamerough canal tide flow study.
Meanwhile, Maritime Safety Queensland general manager Kell Dillon said they continued to monitor the conditions in the passage and around the island.
“This is a complex area. Tidal effects on the coastline are difficult to predict and will change as we have seen with time,” he said.
“We will move navigation aids as required to mark the best available water once channels become more stable.”
A Sunshine Coast Council spokesperson said council was acting to counter erosion and stormwater surge at Golden Beach – aided by its Coastal Hazard Adaptation Strategy and the Bribie Island Breakthrough Action Plan.
“These plans recognise the expected increase in sea level and tidal range along the western side of the Pumicestone Passage as a result of the breakthrough, and present adaptation pathways for community adaptation, planning, modifying infrastructure and coastal engineering,” they said.
Help keep independent and fair Sunshine Coast news coming by subscribing to our free daily news feed. All it requires is your name and email at the bottom of this article.





